Convert JSON to POJO Objects in Java Online
Convert any JSON object to a POJO JAVA class online. Check below panel on how to use this converter and how to deserialize using Jackson librairy.
Here's how you can convert your JSON string to JAVA objects, we will be using the converter and external libraries like Jackson objectmapper to parse our object.
You can find the source code for this example: HERE
1. Copy and paste your JSON in the first code editor and click "Convert"
Make sure that your JSON object is not large (over 5MB) and is formatted. You can use any JSON format validator online.
You can choose from the settings to format the POJOs into properties (get, set methods) or keep it as fields. This step will not affect our deserialization process.
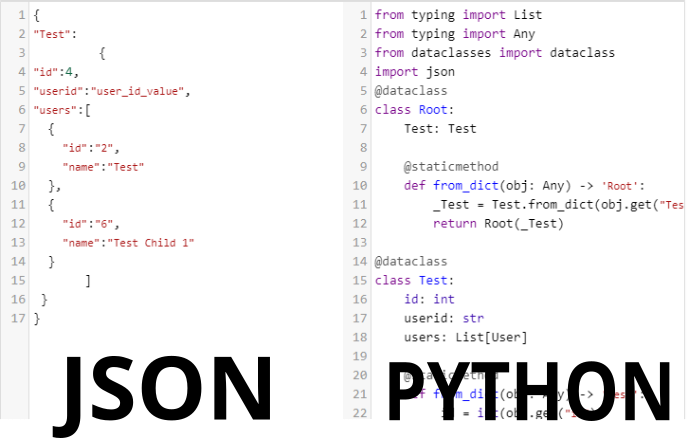
Let's set an example JSON and work with it during the steps:
{
"Test":{
"id":4,
"userid":"user_id_value",
"object": {"prop1" : 1, "prop2" : "test"},
"created_at":"2012-06-02 23:33:90",
"updated_at":"2013-06-02 23:33:90",
"users":[
{
"id":"2",
"name":"Test"
},
{
"id":"6",
"name":"Test Child 1"
}
]
},
"Test2" : {
"Prop2" : "SomeVal2"
}
}
2. Click on "Copy to Clipboard" when the JAVA object classes appear in the second window
This will copy the classes to the clipboard. Here are the classes returned:
public class Object{
public int prop1;
public String prop2;
}
public class User{
public String id;
public String name;
}
public class Test{
public int id;
public String userid;
public Object object;
public String created_at;
public String updated_at;
public List users;
}
public class Test2{
@JsonProperty("Prop2")
public String prop2;
}
public class Root{
@JsonProperty("Test")
public Test test;
@JsonProperty("Test2")
public Test2 test2;
}
You'll notice that there's a "JsonProperty" attribute on some fields that contains the original property name as in the JSON object. This is to tell our fellow Jackson that this field in the java class is named differently than in the JSON object.
Note that we will be using the "Root" class to deserialize our JSON child elements. This will take into consideration that you might have two root notes in your JSON object.
3. Import Jackson libraries
Assuming that you have your favorite IDE opened, your next step is to import the Jackson packages and create the classes returned from the tool.
You will need three Jackson packages:
- jackson-core-2.11.1
- jackson-databind-2.11.1
- jackson-annotations-2.11.1
The "jackson-annotations-2.11.1" is used to add the "JsonProperty" attributes. The "jackson-databind-2.11.1" is used to create the ObjectMapper class which will help us in reading the JSON and map it to our Root Object.
Here's a LINK to the Jackson maven repositories. You can import them manually or using maven whichever you prefer. Note that we will not cover how to import packages into your source code in this article.
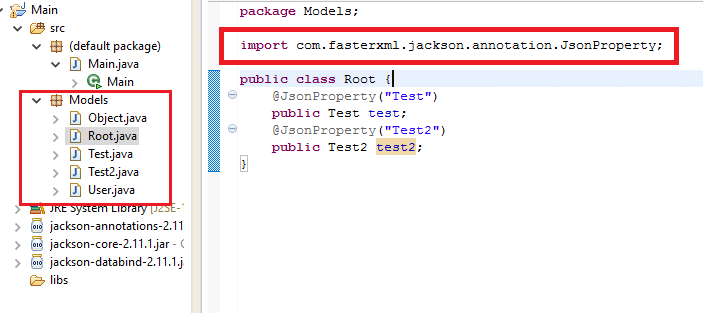
4. Create POJO classes to map your JSON string
We then create our classes and add any imports needed:
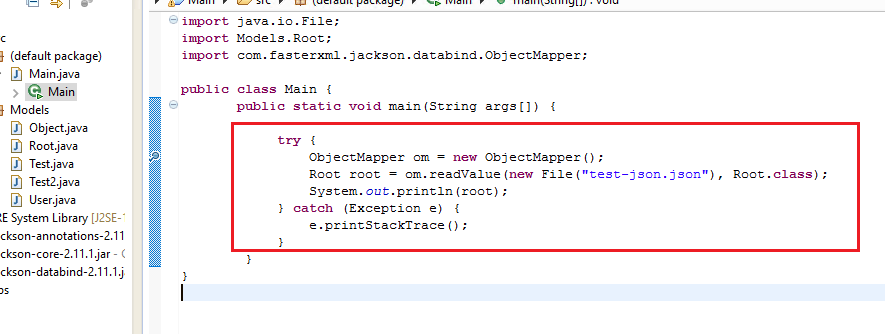
5. Create ObjectMapper class and deserialize into a Root class
Here, we're just creating an ObjectMapper class and calling the "readValue" method. Notice that i'm reading the JSON string from a file system, in your case you might be returning a JSON string from an API or a client.
We then supply the class object of our "Root" class by doing "Root.class".
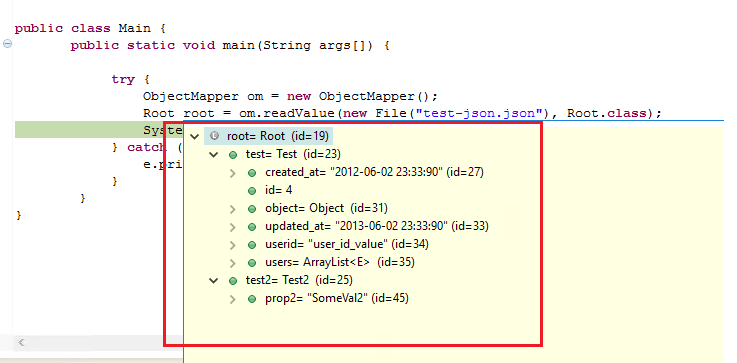
When debugging, you'll notice that our objects have been filled accordingly:
You can find the source code for this example: HERE